Tuned mass damper
A tuned mass damper, also known as an active mass damper (AMD) or harmonic absorber, is a device mounted in structures to reduce the amplitude of mechanical vibrations. Their application can prevent discomfort, damage, or outright structural failure. They are frequently used in power transmission, automobiles, and buildings.
Contents
|
Principle
Tuned mass dampers stabilize against violent motion caused by harmonic vibration. A tuned damper reduces the vibration of a system with a comparatively lightweight component so that the worst-case vibrations are less intense. Roughly speaking practical systems are tuned to either move the main mode away from a troubling excitation frequency, or to add damping to a resonance that is difficult or expensive to damp directly. An example of the latter is a crankshaft torsional damper. Mass dampers are frequently implemented with a frictional or hydraulic component that turns mechanical kinetic energy into heat, like an automotive shock absorber. An electrical analogue is a LCR circuit.
Given a motor with mass 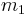 attached via motor mounts to the ground, the motor vibrates as it operates and the soft motor mounts act as a parallel spring and damper,
attached via motor mounts to the ground, the motor vibrates as it operates and the soft motor mounts act as a parallel spring and damper, 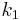 and
and 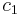 . The force on the motor mounts is
. The force on the motor mounts is 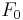 . In order to reduce the maximum force on the motor mounts as the motor operates over a range of speeds, a smaller mass,
. In order to reduce the maximum force on the motor mounts as the motor operates over a range of speeds, a smaller mass, 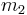 , is connected to
, is connected to 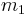 by a spring and a damper,
by a spring and a damper, 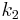 and
and 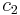 .
. 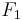 is the effective force on the motor due to its operation.
is the effective force on the motor due to its operation.
The graph shows the effect of a tuned mass damper on a simple spring–mass–damper system, excited by vibrations with an amplitude of one unit of force applied to the main mass, 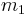 . An important measure of performance is the ratio of the force on the motor mounts to the force vibrating the motor,
. An important measure of performance is the ratio of the force on the motor mounts to the force vibrating the motor, 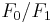 . This assumes that the system is linear, so if the force on the motor were to double, so would the force on the motor mounts. The blue line represents the baseline system, with a maximum response of 9 units of force at around 9 units of frequency. The red line shows the effect of adding a tuned mass of 10% of the baseline mass. It has a maximum response of 5.5, at a frequency of 7. As a side effect, it also has a second normal mode and will vibrate somewhat more than the baseline system at frequencies below about 6 and above about 10.
. This assumes that the system is linear, so if the force on the motor were to double, so would the force on the motor mounts. The blue line represents the baseline system, with a maximum response of 9 units of force at around 9 units of frequency. The red line shows the effect of adding a tuned mass of 10% of the baseline mass. It has a maximum response of 5.5, at a frequency of 7. As a side effect, it also has a second normal mode and will vibrate somewhat more than the baseline system at frequencies below about 6 and above about 10.
The heights of the two peaks can be adjusted by changing the stiffness of the spring in the tuned mass damper. Changing the damping also changes the height of the peaks, in a complex fashion. The split between the two peaks can be changed by altering the mass of the damper (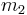 ).
).
The Bode plot is more complex, showing the phase and magnitude of the motion of each mass, for the two cases, relative to F1.
In the plots at right, the black line shows the baseline response (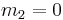 ). Now considering
). Now considering 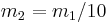 , the blue line shows the motion of the damping mass and the red line shows the motion of the primary mass. The amplitude plot shows that at low frequencies, the damping mass resonates much more than the primary mass. The phase plot shows that at low frequencies, the two masses are in phase. As the frequency increases
, the blue line shows the motion of the damping mass and the red line shows the motion of the primary mass. The amplitude plot shows that at low frequencies, the damping mass resonates much more than the primary mass. The phase plot shows that at low frequencies, the two masses are in phase. As the frequency increases 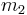 moves out of phase with
moves out of phase with 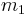 until at around 9.5 Hz it is 180° out of phase with
until at around 9.5 Hz it is 180° out of phase with 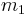 , maximizing the damping effect by maximizing the amplitude of
, maximizing the damping effect by maximizing the amplitude of  , this maximizes the energy dissipated into
, this maximizes the energy dissipated into 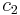 and simultaneously pulls on the primary mass in the same direction as the motor mounts.
and simultaneously pulls on the primary mass in the same direction as the motor mounts.
Mass dampers in automobiles
Motorsport
The tuned mass damper was introduced as part of the suspension system by Renault, on its 2005 F1 car (the R25), at the 2005 Brazilian Grand Prix. It was deemed to be legal at first, and it was in use up to the 2006 German Grand Prix.
At Hockenheim, the mass damper was deemed illegal by the FIA, because the mass was not rigidly attached to the chassis and, due to the influence it had on the pitch attitude of the car, which in turn significantly affected the gap under the car and hence the ground effects of the car, to be a movable aerodynamic device and hence as a consequence, to be illegally influencing the performance of the aerodynamics.
The Stewards of the meeting deemed it legal, but the FIA appealed against that decision. Two weeks later, the FIA International Court of Appeal deemed the mass damper illegal.[1][2]
Production cars
Tuned mass dampers are widely used in production cars, typically on the crankshaft pulley to control torsional vibration and bending modes of the crankshaft, on the driveline for gearwhine, and other noises. They are also used on the exhaust, on the body and on the suspension. Almost all cars will have one mass damper, some may have 10 or more.
Mass dampers in spacecraft
One proposal to reduce vibration on NASA's Ares solid fuel booster is to use 16 tuned mass dampers as part of a design strategy to reduce peak loads from 6g to 0.25 g, the TMDs being responsible for the reduction from 1 g to 0.25 g, the rest being done by conventional vibration isolators between the upper stages and the booster.[3][4]
Dampers in power transmission lines
High-tension lines often have small barbell-shaped Stockbridge dampers hanging from the wires to reduce the high-frequency, low-amplitude oscillation termed flutter.[5][6]
Typically, the dampers are huge concrete blocks or steel bodies mounted in skyscrapers or other structures, and moved in opposition to the resonance frequency oscillations of the structure by means of springs, fluid or pendulums.
Sources of vibration and resonance
Unwanted vibration may be caused by environmental forces acting on a structure, such as wind or earthquake, or by a seemingly innocuous vibration source causing resonance that may be destructive, unpleasant or simply inconvenient.
Earthquakes
The seismic waves caused by an earthquake will make buildings sway and oscillate in various ways depending on the frequency and direction of ground motion, and the height and construction of the building. Seismic activity can cause excessive oscillations of the building which may lead to structural failure. To enhance the building's seismic performance, a proper building design is performed engaging various seismic vibration control technologies.
Mechanical human sources
Masses of people walking up and down stairs at once, or great numbers of people stomping in unison, can cause serious problems in large structures like stadiums if those structures lack damping measures. Vibration caused by heavy industrial machinery, generators and diesel engines can also pose problems to structural integrity, especially if mounted on a steel structure or floor. Large ocean going vessels may employ tuned mass dampers to isolate the vessel from its engine vibration.
Wind
The force of wind against tall buildings can cause the top of skyscrapers to move more than a meter. This motion can be in the form of swaying or twisting, and can cause the upper floors of such buildings to move. Certain angles of wind and aerodynamic properties of a building can accentuate the movement and cause motion sickness in people.
Examples of buildings and structures with tuned mass dampers
Canada
- One Wall Centre in Vancouver — It employs tuned liquid column dampers, at the time of its installation, a unique form of tuned mass damper.
China
Germany
- Berlin Television Tower (Fernsehturm) — tuned mass damper located in the spire.
Ireland
- Dublin Spire in Dublin, Ireland — This narrow slender structure was designed with a tuned mass damper to ensure aerodynamic stability during a wind storm.
Japan
- Akashi-Kaikyō Bridge, between Honshu and Shikoku in Japan, currently the world's longest suspension bridge, uses pendulums within its suspension towers as tuned mass dampers.
- Tokyo Sky Tree, vertically placed two units (total 100 tons) in the housing as atop.
- Yokohama Landmark Tower
Russia
Taiwan
- Taipei 101 skyscraper — Contains one of the world's largest tuned mass dampers, at 730 tons.[7]
United Arab Emirates
- Burj al-Arab in Dubai — 11 tuned mass dampers.
United States of America
- Bally's to Bellagio, Bally's to Caesars Palace, and Treasure Island to The Venetian Pedestrian Bridges in Las Vegas, NV
- Bloomberg Tower/731 Lexington in New York City, NY
- Citigroup Center in New York City, NY — Designed by William LeMessurier and completed in 1977, it was one of the first skyscrapers to use a tuned mass damper to reduce sway. Uses a concrete version.
- Comcast Center in Philadelphia, PA — Contains the largest Tuned Liquid Column Damper (TLCD) in the world at 1,300 tons.[8]
- Grand Canyon Skywalk, AZ
- John Hancock Tower in Boston, MA — A tuned mass damper was added to it after it was built.
- One Rincon Hill South Tower , San Francisco, CA— First building in California to have a liquid tuned mass damper
- Park Tower in Chicago, IL — The first building in the United States to be designed with a tuned mass damper from the outset.
- Random House Tower Uses two liquid filled dampers in New York City, NY
- Theme Building at Los Angeles International Airport Los Angeles, CA
- Trump World Tower in New York City, NY
United Kingdom
- London Millennium Bridge — 'The Wobbly Bridge'
References
- ^ Bishop, Matt (2006). "The Long Interview: Flavio Briatore". F1 Racing (October): 66–76.
- ^ "FIA bans controversial damper system". Pitpass.com. http://www.pitpass.com/fes_php/pitpass_news_item.php?fes_art_id=28765. Retrieved 2010-02-07.
- ^ "Ares I Thrust Oscillation meetings conclude with encouraging data, changes". NASASpaceFlight.com. 2008-12-09. http://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2008/12/ares-i-thrust-oscillation-meetings-encouraging-allowance-for-changes/. Retrieved 2010-02-07.
- ^ "Shock Absorber Plan Set for NASA's New Rocket". SPACE.com. 2008-08-19. http://www.space.com/news/080819-nasa-ares1-vibration-update.html. Retrieved 2010-02-07.
- ^ "On the hysteresis of wire cables in Stockbridge dampers". Cat.inist.fr. http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=13772262. Retrieved 2010-02-07.
- ^ "Cable clingers - 27 October 2007". New Scientist. http://www.newscientist.com/backpage.ns?id=mg19626273.000. Retrieved 2010-02-07.
- ^ Taipei 101's 730-Ton Tuned Mass Damper, Popular Mechanics, May 2005.
- ^ "Comcast Center". http://www.rwdi.com/cms/publications/84/pp_comcast_center.pdf. Retrieved 2010-02-07.